4. Feast and first-born
The tenth plague was that every first-born boy in every Egyptian family would die. This was the pivotal plague to the whole drama. The tragedy would also happen to the Jews unless they followed God’s instructions. They were to paint the blood of a lamb on their door posts. The angel of death would come to Egypt that night and pass over the houses displaying the mark. For the other households, death would take place at midnight. Interestingly, blood is a scarlet/maroon color, the hardest color to see in the dark.
The blood had additional significance: the Jews were to slaughter a one-year-old ram, fully mature, and after they had put its blood on their door posts they were to take it inside for roasting. So they were both covered by it and fed by it. When we call Jesus the ‘lamb of God’ it can suggest a softer, more docile image than the Bible intends, for he is actually the ‘ram of God’, which gives a more robust picture. The Jews were to eat the meat standing up, dressed and ready to leave at a moment’s notice. They were told to take emergency rations of unleavened bread. They were to leave Egypt that very night.
The Jews continue to keep the feast of the Passover to this day. At a particular moment in the evening, the youngest member of the family has to ask, ‘What does all this mean?’ The oldest member of the family replies, ‘This is what God did on the night when every first-born boy died and we were saved because of the blood of the ram.’ Thus they are reminded that the first-born needs to be redeemed in every generation.
5. Delivered and drowned
There are three possibilities for the route taken by the Israelites when they left Egypt, indicated on the map overleaf.
The first is known as the northern route. This suggests that they went through a row of sandbanks in a shallow part of the Mediterranean. Maps of Egypt show sandbanks marked at a place called Lake Sirbonis. Their route then takes them to Kadesh Barnea. But they could not have been followed by the Egyptian chariots across the sandbanks, so this seems unlikely.
The second theory is that they went straight across through the Mitler Pass to Kadesh. But there was a line of fortresses (where the Suez Canal is today) built across there, against any invasion from the east. So the Israelites would have had to get through that line of fortresses. They were not armed and able to fight, so this route is very unlikely also.
The third possibility was the southern route down to Mount Sinai, where Moses had been a shepherd for 40 years. This is the most likely, for Moses knew this country. The location of Mount Sinai is uncertain, but all the tradition in the Middle East puts Sinai in the south. The Israelites left Goshen and came south. Pharaoh would only let them go into the desert, thinking that he could always bring them back from there. Having camped, they were hidden from the Egyptians by a cloud God had sent.
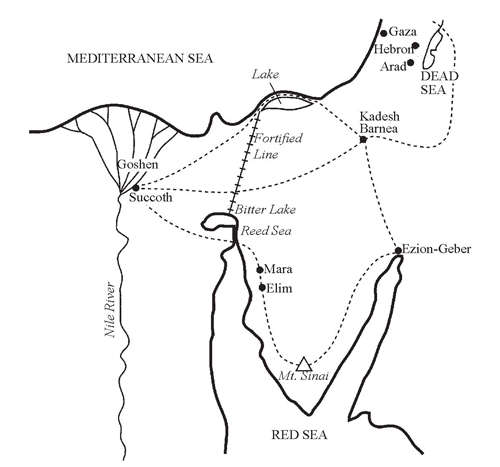
As regards the actual crossing of the sea, the Bible does not say that God divided the Red Sea, but that he sent an east wind which divided the water. But how could an east wind divide a sea?
If we were to examine the area in detail we would see that years ago the Great Bitter Lakes were actually joined up to what we call the Red Sea (see diagram below). They were joined up by a shallow, marshy channel called the ‘Reed Sea’ and in fact the Hebrew suggests the ‘Reed Sea’ is a more likely name than the ‘Red Sea’. The fortified line came right down to the Bitter Lake.
If this was where the Hebrews crossed, there are two natural forces which could have divided the sea. A strong east wind could drive the water to the west end of the Great Bitter Lake, an ebb tide also pulling it south.
This does not explain the miracle at all. How did the east wind just happen to come at the right time? In looking at it in such a down-to-earth way, we are not trying to explain away the miracle. Rather we are showing that it is a miracle of ‘coincidence’. In fact, the Bible tells us that there is no such thing as ‘coincidence’, but only ‘providence’.
The most striking fact about this crossing of the Red Sea or Reed Sea is that it happened on the third day after the Passover lamb was killed. The Israelites’ liberation came on the third day after the Passover lamb. Furthermore, the book of Exodus tells us the very hour when the Passover lamb had to be slaughtered: 3.00 p.m. On the third day after that the Israelites finally escape. They are free of Pharaoh and will never see him again. We will note later some parallels with events in the New Testament.

6. Provided and protected
The desert region over which the Israelites travelled was unable to support human life. It was not the ideal place to take 2.5 million people plus animals.
There were both external and internal problems for Moses, therefore, the most basic being the physical need for food and water. Every morning God provided food for them. They found it lying on the ground when they awoke. It was known as ‘What is it?’ in Hebrew – Manna. Every day there were 900 tons of it. It was literally bread from heaven, a theme revisited later in the Bible.
Though living comfortably on manna, the Israelites complained that they were not getting any meat. They had been used to a high-protein diet in Egypt. So God sent a flock of quails, so many that they lay 1.5 metres deep on the desert floor. The people ate quails until they were sick of them!
They also had a problem with water. The first oasis they came to was Marah. Although the place provided water, it was undrinkable – until it became fresh through a miracle. The next place, Elim, had fresh water from the start. The quantities required were considerable – at least 2 million gallons a day would be needed for that number of animals and people. Later they would get water from rock reservoirs. Perhaps one of the biggest miracles of their providential journey was that their sandals never wore out. Rocks even today wreck rubber tires on vehicles, yet these sandals lasted 40 years!
Moses also faced internal difficulties. Given the enormous numbers, it is no wonder that one of the biggest problems Moses had was judging disputes between the people. We are told that this could go on all day, to the point where Moses became exhausted. It needed his father-in-law Jethro to suggest a delegation of responsibility, whereby Moses appointed 70 elders to assist in the work.
Follow David Pawson!